내부클래스: 클래스나 인터페이스 내에서 선언된 클래스.
1. instance 내부 클래스
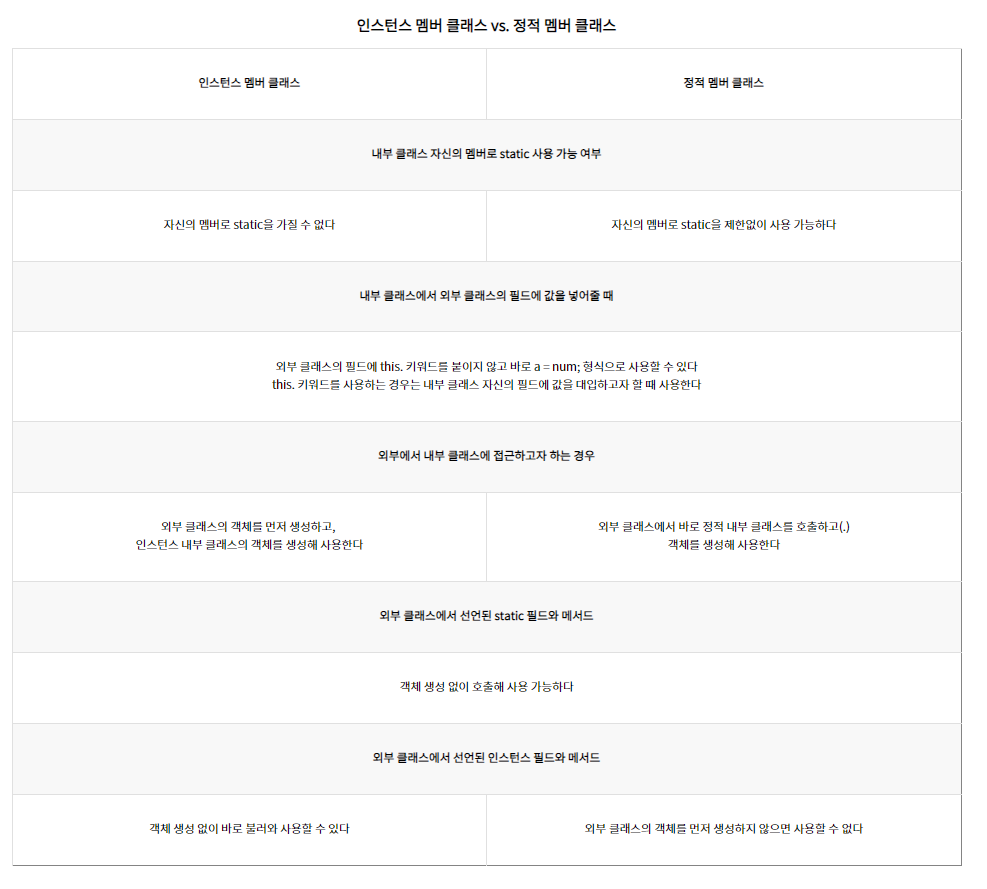
- static 키워드 없이 외부클래스의 멤버로 선언되는 클래스
- 인스턴스 필드와 메서드만 선언 가능
- static 메서드는 가질 수 없다.
public class GameSetup {
private int device_width;
private int device_height;
// 멤버 내부클래스(인스턴스 클래스)
public class GamePlay{
private int menu=1;
public void execute() {
System.out.println(device_width); // 외부클래스의 필드를 불러오기 위해 this가 필요없음
System.out.println(device_height);
System.out.println("이렇듯 단말기의 환경을 곧 바로 갖다 사용할 수 있는 장점이 있음.");
System.out.println("게임 진행");
}
}
}
2. static 내부 클래스
- static 키워드를 갖고 외부클래스의 멤버로 선언되는 클래스
- 클래스의 멤버로 모든 종류의 필드와 메서드를 사용 가능
- DTO의 builder 패턴 만들 때 사용
// DTO클래스
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
public class UserDTO implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 100L;
private int id;
private String name;
private String emai;
public UserDTO() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public UserDTO(int id, String name, String emai) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.emai = emai;
}
public UserDTO(Builder builder) {
this.id = builder.id;
this.name=builder.name;
this.emai=builder.emai;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmai() {
return emai;
}
public void setEmai(String emai) {
this.emai = emai;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
UserDTO other = (UserDTO) obj;
return id == other.id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserDTO [id=" + id + "]";
}
// static 내부클래스
public static class Builder{
private int id;
private String name;
private String emai;
public Builder() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Builder setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public Builder setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Builder setEmai(String emai) {
this.emai = emai;
return this;
}
public UserDTO build() {
return new UserDTO(this);
}
}
}
==============================================================
public class MainEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserDTO dto= new UserDTO.Builder()
.setId(1)
.setName("홍")
.setEmai("a@a.com")
.build();
}
}
3. local 내부 클래스
- 메서드(생성자) 내부에서 선언되는 클래스
- 메서드(생성자)안에 직접적으로 메서드를 생성할 수 없음.
- 하지만 로컬내부클래스를 이용하면 간접적으로 메서드 생성이 가능.
- 접근제한자는 붙일 수 없음(메서드 내부에서만 사용되는 클래스이기 때문에 접근 제한의 의미가 없음)
- static키워드 역시 사용 불가
- 로컬은 외부로부터 철저하게 벽을 쌓고 있으므로 안전함(보안적으로 매우 우수)
public class TestEx01 {
// 디폴트생성자
public TestEx01() {
// void me1() { // local 영역에서는 메서드를 직접적으로 생성할 수 없음
//
// }
// 지역 내부클래스(local이기에 접근제한자 없음.)
class Inner03{
int a;
private int b;
public void me1() { // 로컬내부클래스를 이용하면, 간접적으로 메서드 생성 가능
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
Inner03 obj3 = new Inner03();
obj3.me1();
}
}
4. 익명의 내부 클래스
- new 연산자로 객체 생성과 동시에 선언되는 클래스
- 클래스의 형식(class 키워드 없이)을 이용하지 않고 곧 바로 객체 생성
- 클래스를 이용해서 단 하나의 객체를 만들 때 사용.(일회용)
public interface Inter1 {
void v1();
void v2(int a);
}
=======================================================
public class NextPage {
public int v;
// 익명의 내부클래스를 멤버변수처럼 선언(멤버변수와 같은 범위로 사용 가능)
public Inter1 aa = new Inter1() { // Inter1이라는 익명의 내부클래스 생성
@Override
public void v2(int a) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void v1() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
public void mee() {
aa.v1(); // 여기서도 사용 가능(멤버변수의 범위와 같기 때문)
}
}
장점
- 클래스를 논리적으로 그룹화할 수 있다.
- 클래스가 하나의 특정 클래스와만 관계를 맺는다면 내부클래스를 사용하여 편리하게 관리 가능.
- private 을 사용하더라도 내부클래스를 이용하면 getters/setters 사용 없이 외부클래스의 멤버에 접근 가능하다.
-> 이렇게 사용하면서 자기 자신의 접근 제한 역시 private으로 설정해 외부로부터 접근을 차단할 수 있다.
-> 외부 데이터로부터 보호 가능
- 가독성이 좋고 유지 관리가 쉬운 코드 작성이 가능하다.
'자바(java)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Random (0) | 2023.03.14 |
|---|---|
| 예외처리(Exception) (1) | 2023.03.13 |
| Enum(Enumeration) (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| 람다식(Lambda) (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| DTO(Data Transfer Object) 클래스 (0) | 2023.03.09 |
